What is Forging and Why It Matters?
Well, let me tell ya something, forging ain’t a newfangled thing at all. It’s somethin’ folks been doin’ for centuries! They take metal—most often steel or iron—and press it together with a lot of force to make things like tools, car parts, and even fancy jewelry. Now, the trick to forgoin’ is in how it’s done. They ain’t just hammerin’ away willy-nilly. There’s a whole process behind it, y’know? You got different types of metals, different methods of hammerin’, and well, different results dependin’ on how hot or cold that metal is when you start workin’ it. But don’t you worry, I’ll explain it all in simple words, so we all understand.
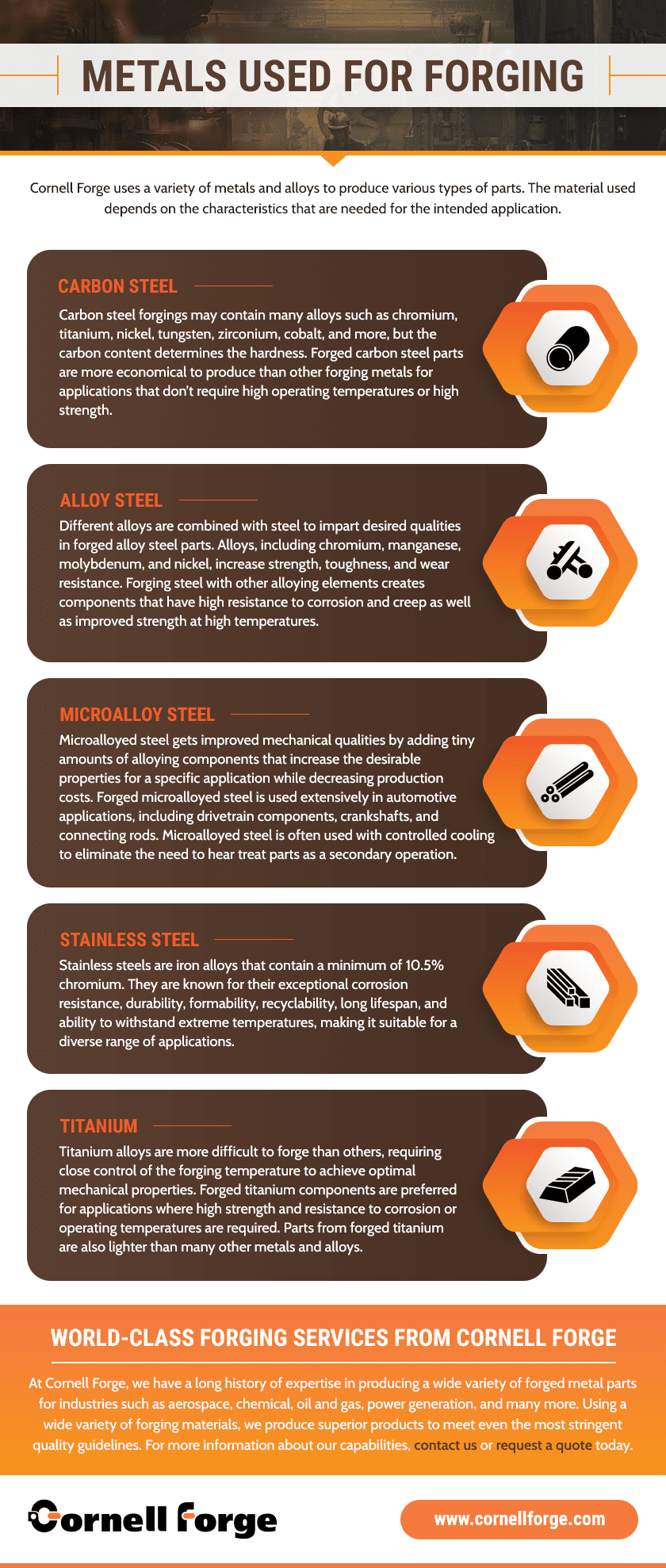

What Materials Can Be Used in Forging?
When it comes to the materials used in forgoin’, it’s like pickin’ what kind of flour to use for makin’ bread. You got choices, but not all choices are right for every job. The most common material for forgoin’ is steel. Yep, that’s the one they use the most. Steel comes in different kinds—carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, you name it. If you want somethin’ a little stronger, you go for alloys like titanium or nickel. They use these metals in a lot of big jobs, like for makin’ parts for airplanes, cars, and such. And don’t forget about aluminum! It’s light but still tough. It’s got a lot of uses, too, especially in things like lightweight frames and even in some kitchen tools!
Sometimes they use fancy stuff like copper or brass, too. I reckon they use copper ‘cause it’s good for conductin’ heat and electricity. And brass? Well, that’s for things like locks or even musical instruments. It’s shiny and does a fine job when you want a pretty look along with durability. So, all these metals come into play dependin’ on what kinda thing you’re makin’.
Hot Forging vs Cold Forging
Now, let’s talk about how hot or cold that metal needs to be when you’re forgoin’. You got two main ways: hot forgoin’ and cold forgoin’. Hot forgoin’ is when you heat up the metal to a high temperature before you hammer it into shape. The heat makes the metal soft and easier to shape, and it helps get rid of any air pockets or flaws inside the metal. It’s like when you make dough—you gotta warm it up to make it stretch easy, right?
Cold forgoin’, on the other hand, is when you shape the metal without heating it up much. It’s a lot harder, but it works fine for smaller parts or parts that don’t need to be too big. People use cold forgoin’ for things like bolts or small machine parts, where the metal doesn’t need to be too fancy. But in general, most folks stick to hot forgoin’—especially when they’re makin’ big ol’ parts like car axles or engine blocks.
Why Forging Is So Good
What’s so good about forgoin’, you ask? Well, let me tell ya—when you forge metal, you get somethin’ stronger than if you just cast it or weld it together. The metal gets compressed, and that helps the grain structure stay tight, which means fewer weak spots. It’s like makin’ cornbread with good, fresh ingredients—you get a stronger, better result! Forged metal is tougher, less likely to crack, and it’s got a smoother surface. So, when you need something to last a long time—like parts in a car or machinery—you better believe forged metal is the way to go.
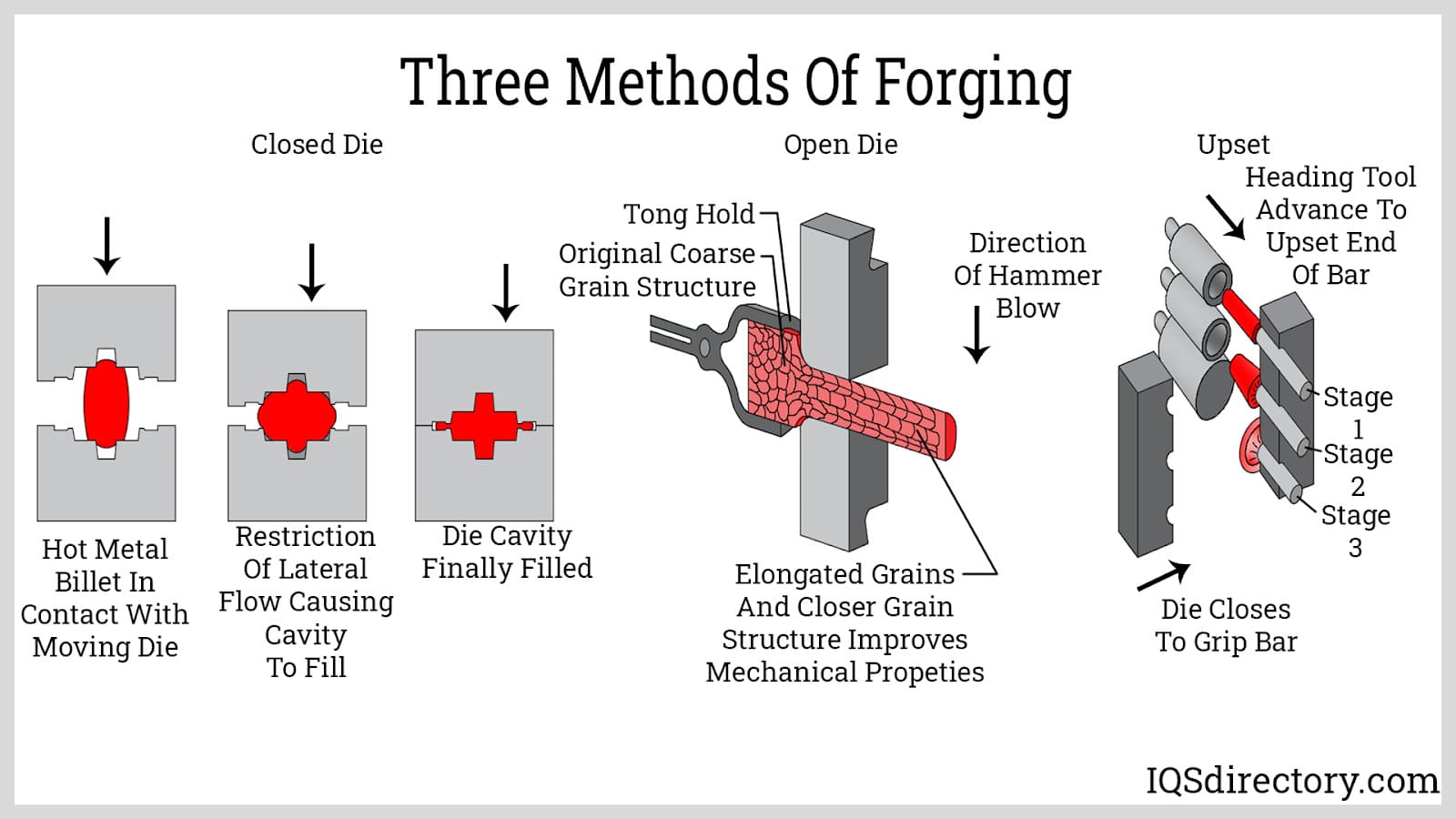

What Tools Do You Need for Forging?
Well, for starters, you need a forge! That’s like the oven where you heat the metal up. Some folks got a simple charcoal forge, others got fancy gas-powered ones. But either way, it’s gotta get hot enough to make the metal soft. Then, you need a hammer, or better yet, a power hammer, ‘cause you ain’t gonna be doin’ this all by yourself with a regular hammer. A power hammer’s like a big ol’ machine that helps strike the metal without you breakin’ your back.
Some folks use presses instead of hammers, too. It’s all about how much pressure you need to apply. But don’t forget, if you’re gonna use a press, you also gotta have a good die—kind of like a mold—to make sure the metal comes out the way you want it. Think of it like bakin’ a cake—ya need the right pan to shape it right!
Forging Steel and Other Metals
As I said before, steel is the most common material folks use in forgoin’. And when it comes to steel, there’s a bunch of different kinds! Some steel’s made to take high temperatures, others are better for tougher jobs. One kind of steel often used for forgoin’ is called H13. It’s tough and can handle high heat, so it’s good for stuff like moldin’ or makin’ tools. L6 steel’s another one folks use—it’s tough, and holds up real well under stress. Then, there’s also what they call “tool steel.” This stuff is made specifically for makin’ tools, like knives or drills.
And if you’re wonderin’ what about things like aluminum or titanium, well, they got their own benefits. Titanium’s lighter than steel, but just as strong, so it’s used in planes or rockets. Aluminum’s also light, but it doesn’t hold up as well to heat. But for certain things, like frames or body parts on a car, it does just fine!
Conclusion
So, as you can see, forgoin’ ain’t just about hammerin’ metal into shape. It’s about knowin’ what materials work best for what you need and choosin’ the right process to get the job done. Whether you’re heatin’ it up or keepin’ it cold, forgoin’ helps make stronger, longer-lasting parts for all kinds of things. And with all the different metals to choose from, there’s a lotta options to make sure you get exactly what you need. It’s been around for a long time, and it ain’t goin’ anywhere anytime soon!

Tags: [Forging, Materials, Steel, Metalworking, Hot Forging, Cold Forging, Alloy Steel, Forged Metal, Manufacturing]